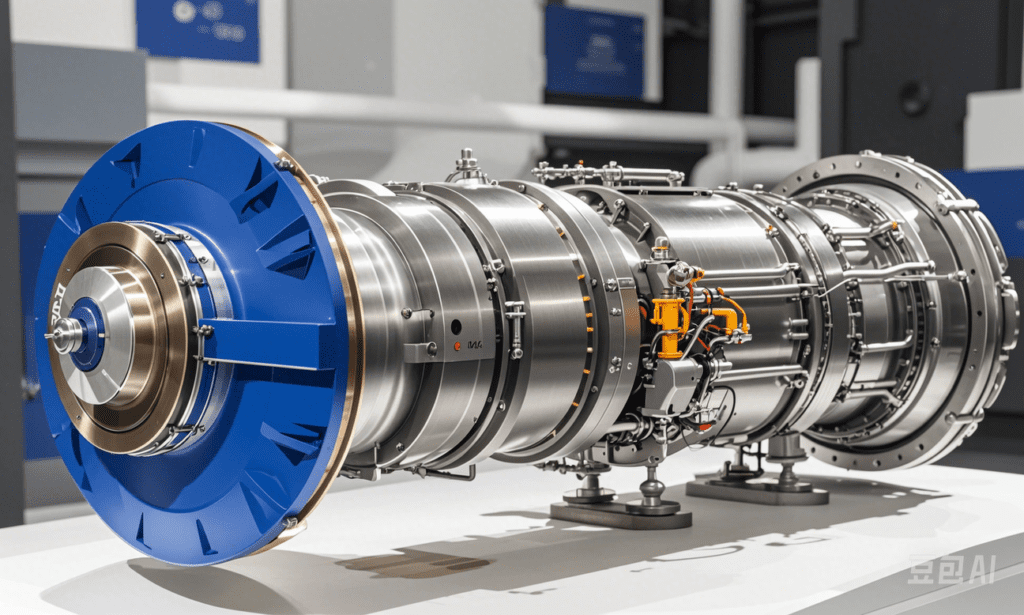
What is a gas turbine?
Answer: A gas turbine is an internal combustion power machine that uses a continuously flowing gas as a working fluid to drive the impeller to rotate at high speed, converting the energy of the fuel into useful work. It is a rotating impeller heat engine.
What thermodynamic processes are included in the ideal simple cycle of gas turbine (Braton cycle)?
Answer: The Brayton cycle includes four processes:
- (1) Isoentropic compression (or adiabatic compression) in the compressor;
- (2) Constant-pressure heating in the combustion chamber;
- (3) Isoentropic expansion (or adiabatic expansion) in the turbine;
- (4) Constant-pressure heat release in the atmosphere.
What is a simple cycle? What is a combined cycle?
Answer: A simple cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that utilizes the processes of compression, combustion, and expansion. A combined cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that combines a gas turbine with a steam cycle or a Rankine cycle of other fluids.
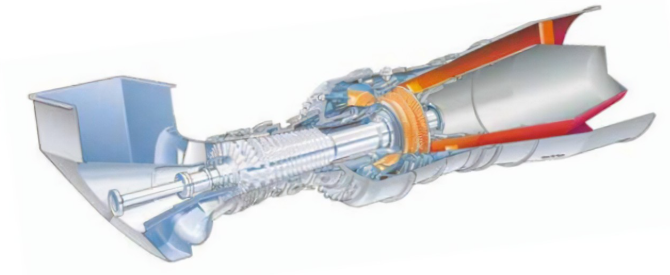
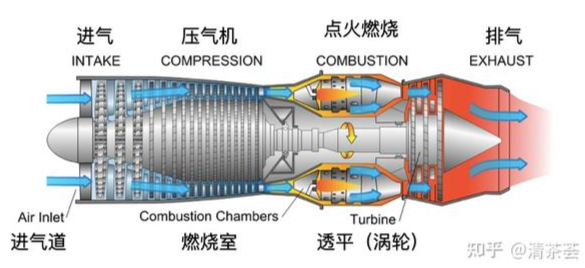
What is a gas turbine compressor? What is a combustion chamber? What is a turbine?
Answer: The gas turbine compressor is a gas turbine component that uses mechanical power to increase the pressure of the working fluid, accompanied by an increase in temperature.
The combustion chamber is a component in which fuel and air are mixed and burned to produce high-temperature combustion gas. The turbine is a rotary power machine that expands the working fluid in the blade channel and converts heat energy into mechanical energy.

What is a gas-steam combined cycle? What are its advantages?
Answer: Gas-steam combined cycle means that the exhaust heat of the gas turbine is used to generate steam in the Rankine cycle. The excellent thermodynamic performance of this cycle is due to the combination of the best thermodynamic characteristics of each cycle, so it has a high thermal efficiency, that is, heat can be added at a higher temperature in the gas turbine cycle, while heat can be released at a lower temperature in the Rankine cycle.
What is the gas turbine temperature ratio? What is the compressor pressure ratio?
Answer: The temperature ratio refers to the ratio of the highest cycle temperature t3* (initial gas temperature) to the lowest temperature t1*.
The ratio of the gas pressure P2* at the compressor outlet to the gas pressure P1* at the inlet reflects the degree of compression of the working fluid.
What is gas turbine specific power? What is the specific power unit?
Answer: The specific power of a gas turbine refers to the mechanical work (electrical work) or net work that can be output to the outside after completing a cycle in the gas turbine for every 1 kg of air entering the gas turbine compressor.
What is the intake duct of a gas turbine? What is the exhaust duct?
Answer: The inlet duct of a gas turbine refers to the pipe that introduces the working fluid into the compressor inlet flange. The exhaust duct refers to the pipe that guides the working fluid from the gas turbine to the atmosphere or the heat recovery device or precooler.
What is the initial temperature of gas turbine gas?
Answer: The initial temperature of gas turbine gas is the average stagnation temperature of the gas at the trailing edge plane of the first stage nozzle in the gas turbine.

What is the standard rated output power of a gas turbine?
Answer: The standard rated power of a gas turbine refers to the maximum continuous power at the generator output terminal when it operates continuously under IS0 conditions, that is, an ambient temperature of 15°C, sea level, a relative humidity of 60%, and burning natural gas.
Briefly describe the gas pressurization process in an axial flow compressor?
Answer: The outside world transfers a certain amount of compression shaft work lc to the air flowing through the moving blades on the working impeller, increasing the absolute velocity kinetic energy of the airflow and reducing the relative velocity kinetic energy of the airflow, so as to increase the pressure of the air.
Then, the high-speed airflow flowing out of the moving blades gradually slows down in the stationary blades, so that part of the absolute velocity kinetic energy of the airflow can be further converted into the pressure potential energy of the gas, so that the pressure of the gas can be further increased.


What is a Steam Injection Gas Turbine?
Answer: A steam-injected gas turbine uses the exhaust gas of the gas turbine to pass into a waste heat boiler to generate steam, and then injects the rest (or part of it) into the combustion chamber and high and low pressure turbines to form a gas-steam mixture, which expands in the turbine to do work.
What is IGCC technology? What are its two components?
Answer: IGCC technology is the integrated coal-to-gas combined cycle technology, which refers to an advanced power system that combines coal gasification technology with an efficient combined cycle. It consists of two major parts, namely the coal gasification and purification part and the gas-steam combined cycle power generation part.
What is a combined heat, power and cooling system?
Answer: The so-called combined heat, power and cooling system is an integrated system that adds refrigeration equipment after the cogeneration unit, uses the waste heat or electricity (or shaft power) generated by the heat unit to drive the refrigeration unit to provide cooling to users.
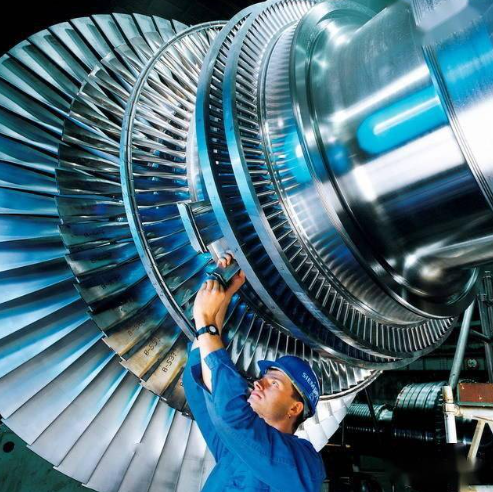
What are the two general categories of compressors? What are their characteristics?
Answer: Axial flow compressor: large flow and high efficiency, widely used in large and medium-sized gas turbines.
Centrifugal compressor: small air flow, higher efficiency than axial flow, simplified unit structure, mainly used in small power gas turbines.
Briefly describe the main performance parameters of axial flow compressor?
Answer: The main parameters of axial flow compressor performance are:
- (1) air flow;
- (2) compression ratio;
- (3) compressor constant efficiency;
- (4) compressor input power.
How to define compressor characteristic line and turbine characteristic line?
Answer: The general characteristic curve of the gas turbine compressor is used to represent the relationship between the performance parameters (speed, pressure ratio, flow rate, efficiency, etc.) of the compressor under different working conditions. The turbine characteristic curve is used to represent the relationship between the performance parameters (speed, expansion ratio, flow rate, efficiency, etc.) under different working conditions.
What effects does fouling and fouling of axial compressor blades have on gas turbine performance?
Answer: Dirt and fouling of the axial flow compressor blades will change the aerodynamic performance of the compressor blades, resulting in a decrease in the compressor flow, pressure ratio and efficiency, and a change in the performance curve. On the one hand, the decrease in compressor performance causes a decrease in the output and efficiency of the engine; on the other hand, the change in the compressor performance curve will cause the unit’s operating line to approach the surge boundary, that is, the surge margin is reduced, making it more likely to cause surge. Dirt and fouling of the axial flow compressor will cause the compressor’s air flow, internal efficiency and pressure ratio to decrease.
What is friction loss in a gas turbine compressor?
Answer: The friction loss of a gas turbine compressor is the energy loss caused by the friction between the air and the blade surface, cylinder wall and air particles when the air flows through the compressor.
What are the internal energy losses of an axial flow compressor?
Answer: The internal energy losses of an axial flow compressor include:
- (1) Friction loss and eddy current loss in the flow section of the compressor.
- (2) Leakage loss in the radial clearance.
- (3) Leakage loss in the internal gas seal between stages.
- (4) Frictional blast loss between the end pressure of the working impeller or drum and the airflow.
