1.Forging Turbine Blade Preparation before forging
- (1) Material preparation: According to the application environment and performance requirements of the blades provided by customers, choose the appropriate high-temperature alloy materials, such as nickel-based alloy, cobalt-based alloy, titanium alloy and so on. The raw material is smelted and then cast to make a forging blank.
- (2)Billet preheating: preheat the forged turbine blade billet to a suitable temperature to facilitate plastic deformation. The temperature is usually between 1000-1200 degrees Celsius, depending on the characteristics of our products, and the use and needs of each customer are different.
- (3) Mold preparation: According to the shape and size of the blade, design and process the corresponding forging mold, usually we use high-strength steel or heat-resistant alloy production, and our factory will also carry out strict heat treatment and surface treatment of the mold to ensure its hardness, wear resistance and dimensional accuracy.
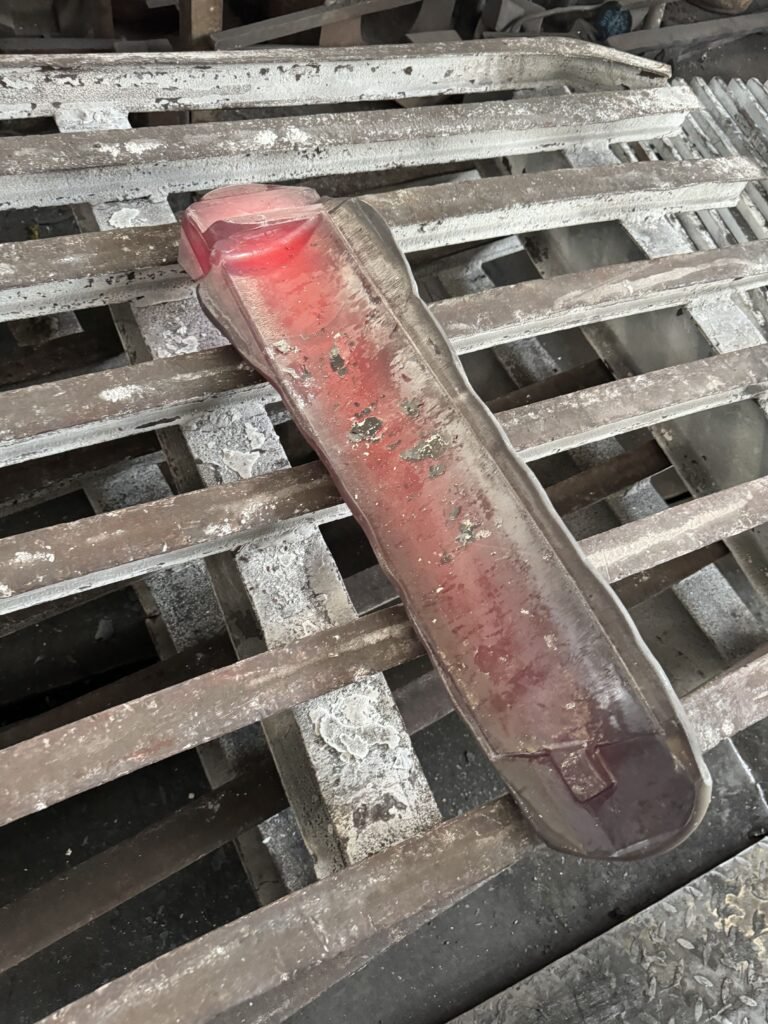
2. Forging process
- (1)Initial forging: Put the preheated billet into the forging die, use the forging machine for initial forging and preliminary forming. We will choose free forging or die forging according to the material and shape required by customers, so as to initially shape the billet into the basic shape of the blade.
- (2)Precision forging: According to the shape and size requirements of customers’ blades, die-forging is adopted to further improve the precision and surface quality of blades.
- (3) Intermediate heat treatment: In the precision forging process, we will perform intermediate heat treatment in specific equipment as required to eliminate stress and improve the toughness of the blade.
- (4)Cutting and dressing: cut the forged blade, remove excess material, and trim the blade to ensure that the size and shape of the blade meet the design requirements.


3.machining process:
- (1)Blank processing: the forged blade is used as a blank for preliminary processing, such as cutting, drilling, etc., to prepare for subsequent precision machining.
- (2)Finishing: According to the design requirements of the blade, the blank is finished, such as milling, turning, grinding, etc., in order to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- (3)Blade root processing: the blade root usually requires special processing technology, such as rolling, spinning, etc., to improve the strength and fatigue performance of the root.
- (4)Blade aerodynamic shape processing: Blade aerodynamic shape needs to be processed using high-precision machine tools and special tools to ensure that the aerodynamic performance of the blade meets the design requirements.
- (5)Blade cooling hole processing: The blade cooling hole needs to be processed using special processing equipment and technology to ensure that the size, shape and position of the cooling hole meet the design requirements.
- (6)Surface treatment: Surface treatment of the blade as required, such as shot peening, coating treatment, etc., but our tolerance should be controlled within the scope of customer requirements.

4. Detection
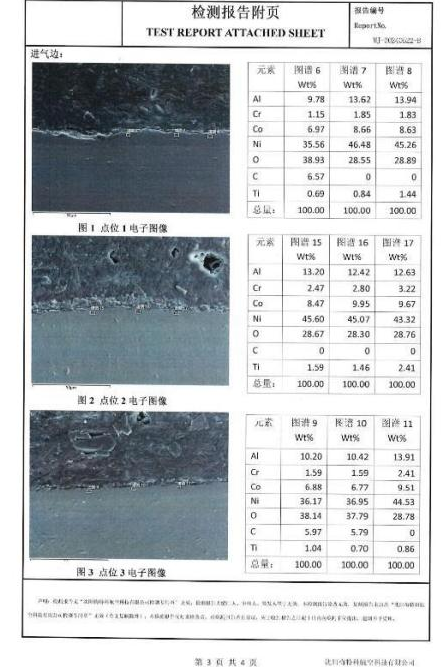
- In the forging process and after machining, there will be inspection and detection of this step, mainly chemical composition inspection, mechanical inspection, tensile strength of raw materials, yield strength, elongation, hardness and other mechanical performance indicators, to ensure the integrity of the turbine blade inside and outside, to avoid defects and mechanical performance substandard problems. In the machining process, we will use dimensional inspection, surface quality inspection and geometric size inspection to avoid the occurrence of substandard specifications, substandard coatings or substandard tolerances.
- This is a big reveal of the process of forging turbine blades for one of our Russian customers, our machining equipment and forging equipment and technicians are very capable.

We are specialized in casting and forging turbine products. If you have customized requirements, you can contact us directly.
