Basic Concepts
According to the “Gas Turbine Vocabulary” (GB/T 15135-2018), a gas turbine refers to a continuous-flow rotating machine (single machine) that converts thermal energy into mechanical work, including a compressor, equipment for heating the working fluid (such as a combustion chamber), a turbine, a control system and auxiliary equipment.
Industrial gas turbine engines, generally referred to as gas turbines or turbines, industrial gas engines, are essentially the same thing as aviation turbine gas engines (referred to as aviation engines), but the application scenarios are slightly different. They compress high-pressure gas into a combustion chamber, and through the reaction of chemical energy, convert the chemical energy into mechanical work through a turbine.
As an energy conversion device, a gas turbine is an aircraft engine that converts aviation kerosene into mechanical energy for the propeller when flying in the sky; a gas turbine used on the ground converts natural gas and oil into mechanical energy for the generator.
Steam turbines, internal combustion engines, and gas turbines were first developed for use on warships. Steam turbines were used before World War I, internal combustion engines were used during World War I and World War II, and gas turbines for warships were developed after World War II. They were modified from aircraft engines and were mainly used on large surface ships.

Gas turbines have several characteristics:
- First, the theoretical energy conversion efficiency can reach 88%, which is the device with the highest energy conversion efficiency in the world so far. Fuel cells are said to be able to achieve a conversion efficiency of 90%, but they have not yet been fully commercialized; the theoretical energy conversion efficiency of combustion engines is 88%, which has been tested for decades.
- Second, the combustion temperature of gas turbines is relatively high, and the emission of harmful gases is relatively low.
- Third, the power density is relatively large. A single machine the size of a container can supply energy to a destroyer; two containers are basically enough for the civilian electricity of a county. Steam turbines are very large, such as diesel engines and internal combustion engines with a capacity of more than 10 megawatts, which are basically large devices weighing thousands of tons and tens of meters high.
- Fourth, gas turbines are not like internal combustion engines, which are stroke-type, and work is done once every 4 strokes. Gas turbines work continuously, and the turbine is a vortex line. It is a thermal engine device with the highest energy conversion efficiency, converting chemical energy into thermal energy and mechanical energy.
- In the 1970s, gas turbines entered the US oil industry, giving rise to industrial gas turbines. Aircraft engines require relatively high performance, are relatively sophisticated, and have a relatively short lifespan; industrial engines do not need to reduce weight, are made very sturdy, and require a relatively long lifespan. Around the 1980s, with the development of natural gas, it entered the power industry.
- After World War II, the United States’ technical level was not very high. The earliest acquisition was of Italian companies, which are the capital of rotating equipment in Europe. The typical British company is Rolls-Royce, which makes aircraft engines. Generally, companies that make aircraft engines will make gas turbines. Germany’s Siemens was acquired all over Europe, and also acquired Rolls-Royce’s aircraft modification. Russia’s gas turbines are mainly in cooperation with Ukraine. The designs are all in Russia, and some of the manufacturing bases are in Mariupol, Ukraine.
- In recent decades, only Mitsubishi of Japan has developed a real heavy-duty gas turbine, and Kawasaki makes smaller ones, so there is still a certain threshold. Small and medium-sized gas turbines are mainly GE, especially for military use. The mainstream destroyers are mostly GE, the LM-2500 model. Siemens acquired some of its small gas turbines in Lincoln, UK, with a capacity of less than 15 MW, and some in Finspång, Sweden. The best company in small gas turbines is Solar in the US, which is very close to its customers and has the highest market share in the world for small gas turbines with a capacity of less than 15 MW.
Classification
According to the structural form and output power, gas turbines can be divided into three categories: micro, light and heavy. Among them, micro and light gas turbines can be modified from aircraft engines (also known as “aero-to-gas”), with a power usually within 50MW, and can be used in industrial power generation, ship power, pipeline boosting, tank locomotives, distributed power generation and combined heat and power. Heavy-duty gas turbines have a power of more than 50MW and are mainly used as fixed generators on land, such as urban power grids.
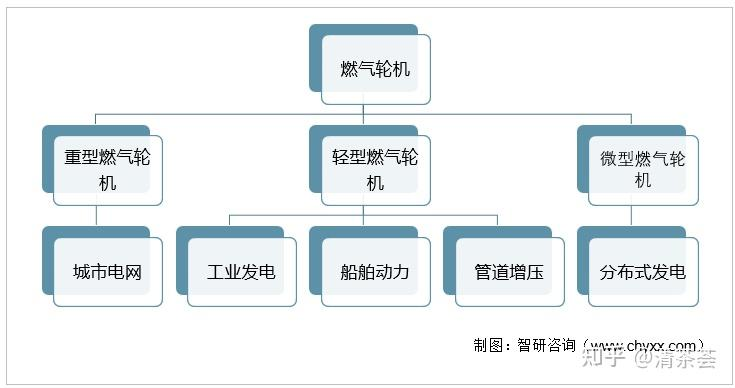

Heavy-duty gas engines are generally classified according to temperature. Class E, F, G, and H correspond to different combustion temperatures. From an engineering perspective, it is more preferable to classify them based on the temperature bearing capacity of the alloy.
In China, it is basically small gas turbines. Small gas turbines are generally classified by structure: single-axis, double-axis, three-axis, aero-modified, industrial, and rarely classified by temperature, because the temperature of small gas turbines is not that high compared to heavy-duty gas turbines. Those with power levels below 30 megawatts are actually equiaxed crystals, that is, E-grade. This is not absolute, and some more advanced ones have reached F-grade. E-grade was trial-produced in China in 1995. About 50 megawatts probably corresponds to F-grade, which is oriented crystal. China trial-produced the grade in 2005, and we now have all these materials. The most advanced gas turbines have reached H-grade, and we now have our second-generation single crystals.
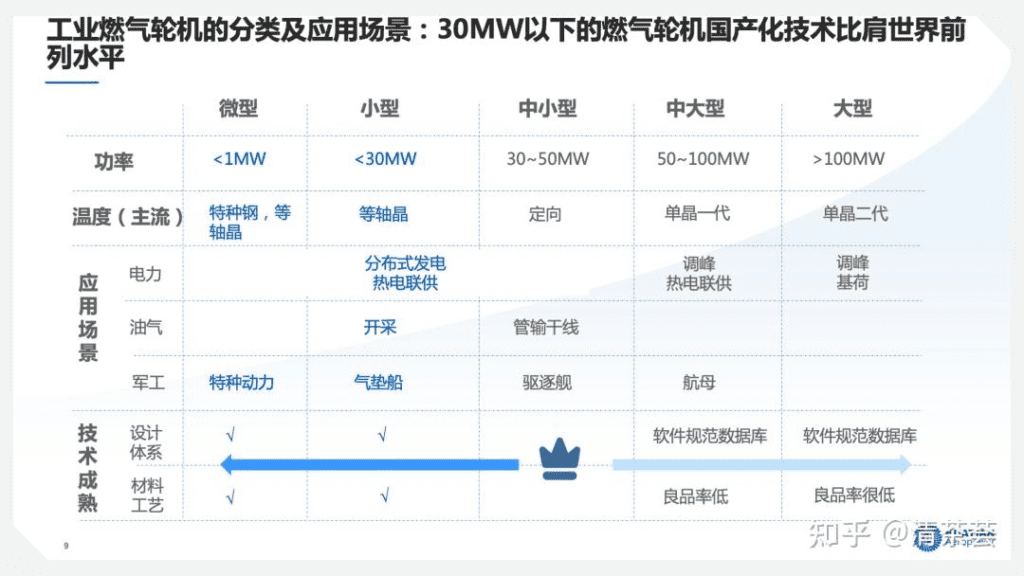

Generally, those below 1 MW are called micro-gas turbines. In fact, micro-gas turbines abroad do not use such good alloys because of the low temperature. They use some special steels, and rarely use equiaxed crystals. Those around 15 MW are called small gas turbines, which mainly use equiaxed crystals. There are also some special companies abroad that use special steels, but because their coatings are particularly good, they are made better. Small and medium-sized 30~50 MW generally use more oriented crystals, that is, F-grade. Larger ones use single crystals of the first and second generations, which are our domestic brands.
Small and medium-sized and micro gas turbines are mostly used in distributed power and combined heat and power. Those below 30 MW and 15 MW are mostly used in Sichuan, and those below 7 MW are mostly used in Chongqing. This is related to the scale of its industrial parks. Those around 30 MW are mostly used in Jiangsu, and those from 50 MW to 100 MW are mostly used in industrial parks in Guangdong, generally for distributed power or combined heat and power. Those above 100 MW are basically used for some large power grid peak regulation or as base load power stations. The oil and gas industry basically uses small ones. In the upstream mining industry, 7 MW and 15 MW are mostly used, and the midstream pipeline transportation is mainly 15 MW and 30 MW.
The design system of gas turbines below 30 MW is relatively mature, and the process material system is also relatively mature. The yield rate of BLAZE can reach 85%. Industrial gas turbines still need to focus on economic performance, technical and economic evaluation, or cost performance, and the main evaluation indicator is the yield rate.
For medium and large-sized gas turbines, we (domestic) have little accumulation of design software, design specifications, and databases of some materials and processes in our design system, so this design system is not very mature and the yield rate is not high. F-level or oriented crystal is a watershed. Below oriented crystal, we are still confident enough to participate in international competition. Above oriented crystal, in the industrial level, we still have a certain gap. This area is handed over to the national team. Several central enterprises are doing some basic research and development, and the investment in basic materials and basic processes is huge.
Industrial Chain
In the upstream of my country’s gas turbine industry chain, manufacturers of high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, composite materials, aluminum alloys and general steel include Gangyan Gaona, Fushun Special Steel, Baoti Group, etc. In the midstream parts and components link, materials are cast, forged or other processes are operated to make turbine blades, shafts and other parts. Blades and other parts are formed by casting process. Major domestic casting and forging manufacturers include Yingliu Co., Ltd., Wanze Co., Ltd., Tunan Co., Ltd., etc. Then, downstream whole machine manufacturers assemble various parts into whole machines. Major manufacturers include AECC, Shanghai Electric, Helan Turbine, Harbin Electric, etc.
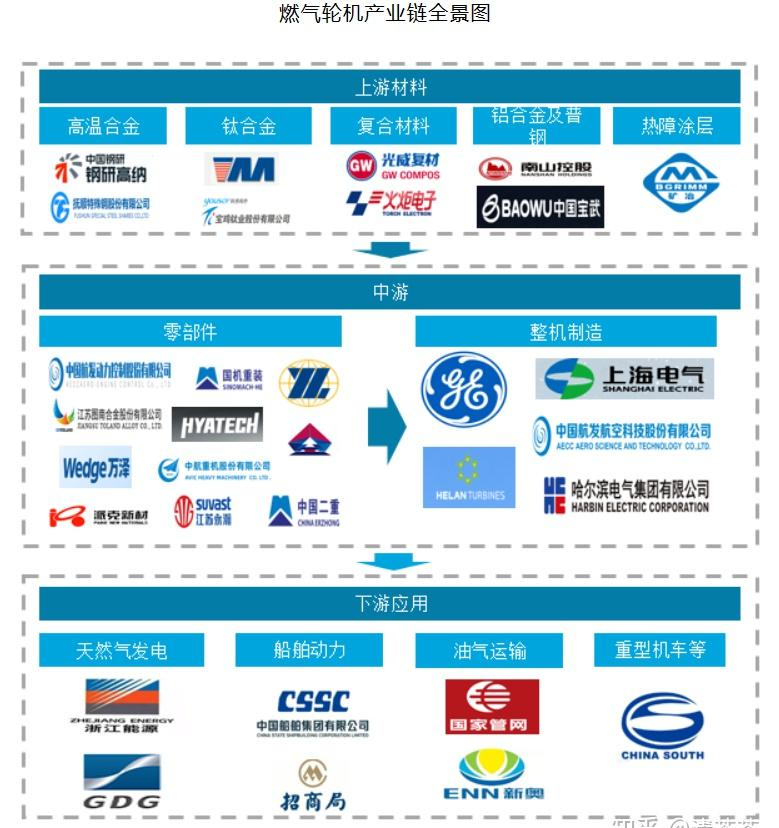

Upstream industries, especially products such as high-temperature alloys, high-temperature titanium alloys, thermal barrier coatings, and advanced ceramic composite materials, have a significant role in promoting the national defense industry and high-end equipment manufacturing. Domestic gas turbines are mainly used for power generation, and a small number are used for water injection, air intake, pressurization in oil and gas fields, and ship and tank power. The focus is on distributed power generation, combined heat and power, natural gas pipeline transportation, ship propulsion, and mechanical drive. aspect. my country’s gas turbines have huge potential markets in distributed energy supply, pressurization stations, industrial power generation and other fields, and policies support the rapid development of the industry. my country’s current large-scale projects such as the “West-to-East Gas Transmission”, “West-to-East Power Transmission” and “South-to-North Water Diversion” as well as the rapid development of my country’s shipbuilding industry have led to a rapid increase in my country’s demand for gas turbines.
Industrial Policy
The 14th Five-Year Plan’s modern energy system also lists gas turbines as a core key technology, basically placing it on the same level as nuclear energy, new power systems, energy storage and hydrogen energy.
State Power Investment Corporation has done two special projects, one is a major project for heavy-duty gas turbines, including hydrogen-blended gas turbines. A pure hydrogen one has been built in Inner Mongolia but has not yet been put into operation. The Jingmen Power Plant has blended 15%. Harbin Electric and Guangdong Electric Group, which is Guangdong Energy Group, have done a hydrogen-blending project in Daya Bay, and Hangzhou Steam Turbine and Siemens have done a hydrogen-blending project in Zhoushan.
Gas turbines are widely used in the West-East Gas Pipeline and on offshore oil platforms. As a military-related enterprise, CNOOC has also been sanctioned by the United States and faces the risk of supply cuts. During the Russian-Ukrainian war, the Siemens gas turbines purchased by Russia were detained when they were sent to Canada for repair, affecting energy security. Localization must be carried out as soon as possible.
Market Space
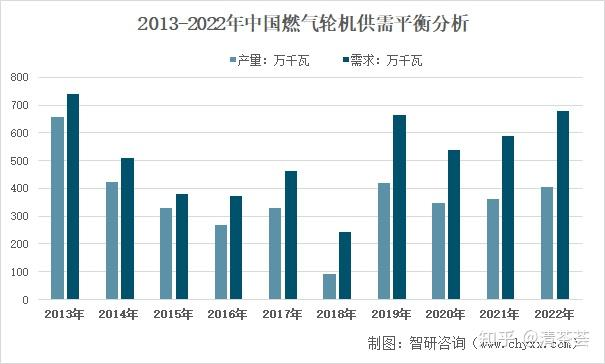
In 2022, my country’s gas turbine production will be 4.0563 million kilowatts, and the demand will be about 6.7986 million kilowatts.

According to statistics, the size of my country’s gas turbine market reached 61.669 billion yuan in 2022, of which the market size of micro gas turbines was 893 million yuan, the market size of light gas turbines was 56.569 billion yuan, and the market size of heavy gas turbines was 4.207 billion yuan.
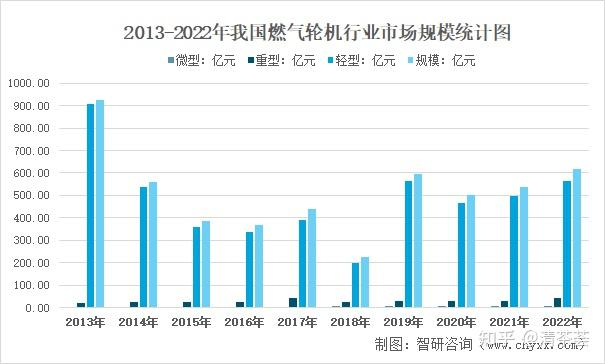

My country now has the ability to independently produce light gas turbines (power below 50MW), and low-end ones can even be exported, but heavy gas turbines (power above 50MW) are still basically dependent on imports, and the core technology is basically monopolized by international manufacturers such as GE in the United States, Mitsubishi in Japan, and Siemens in Germany. There is a risk of being “choked” in the domestic market. According to data from the General Administration of Customs, gas turbine imports in 2022 will be US$4.161 billion and exports will be US$735 million.
The author of this article is employed by BLAZE, a company that specializes in gas turbine accessories.
