The forging process of a gas turbine turbine is a complex and sophisticated process involving multiple steps to ensure that the resulting turbine components can withstand extreme operating conditions such as high temperature, high pressure and high-speed rotation. The following details its main process:
1. Raw material selection and preparation
- Material selection: Turbine materials are usually made of high-performance alloys with high temperature resistance, oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, such as nickel-based alloys (Inconel, Nimonic) and cobalt-based alloys (Stellite).
- Raw material pretreatment: The purchased raw materials need to go through strict quality inspection, including chemical composition, mechanical properties and internal defects inspection, and preheat treatment, the material is heated to close to the forging temperature to prepare for the subsequent forging.

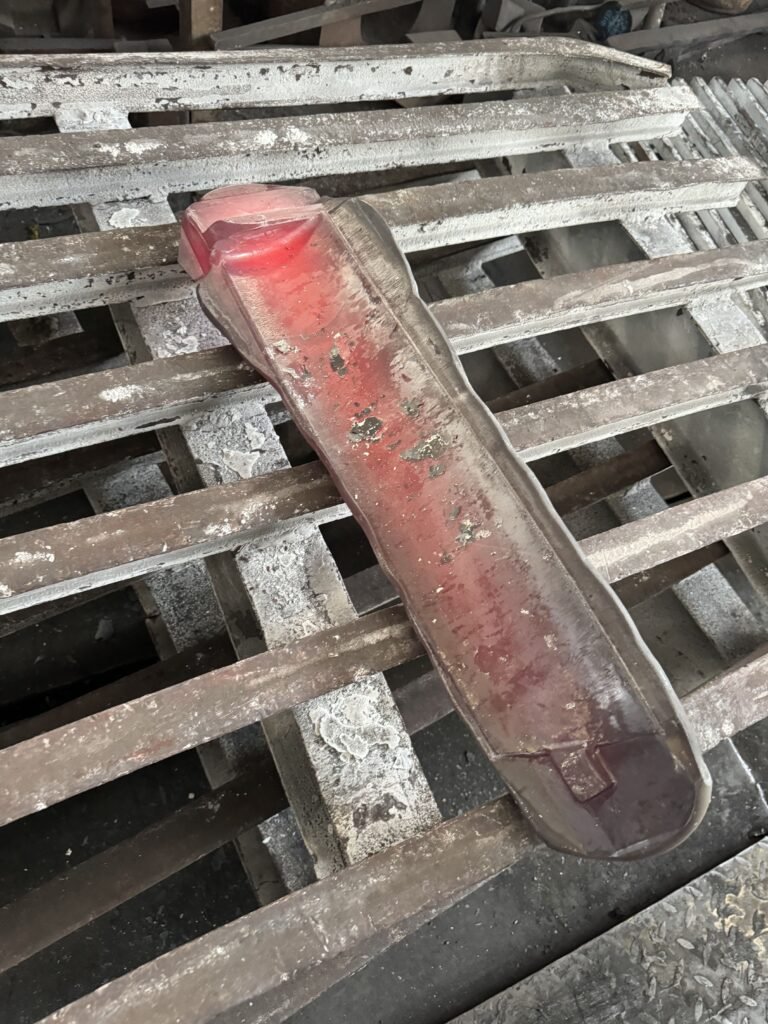
2. Forging process
- Pre-forging: The pre-treated material is preliminarily formed by press or forging hammer, the internal defects are removed, and the organizational structure of the material is adjusted to lay the foundation for subsequent precision forging.
- Precision forging: the pre-forged blank is reheated to forging temperature, and the die forging or free forging process is used to fine shape, and finally the blank is close to the final shape.
- Forging parameter control: Forging requires strict control of temperature, pressure and speed to prevent material strength loss, forming difficulties, surface damage or reduced efficiency.


3. Heat treatment
- Annealing: The forged blank is annealed to eliminate the forging stress, improve the plasticity and toughness of the material, and provide a good basis for subsequent processing.
- Quenching: The annealed blank is quickly heated to the quenching temperature and then quickly cooled to obtain high hardness and wear resistance.
- Tempering: the quenched blank is reheated to the tempering temperature, and slowly cooled after holding for a period of time, reducing the hardness of the material, improving the toughness, and improving the comprehensive performance of the material.


4. CNC processing
- Roughing: The use of milling machines, lathes and other equipment for roughing, cutting the blank into semi-finished products close to the final size and shape.
- Finishing: The use of CNC machining center and other equipment for finishing, processing semi-finished products into the final size and shape of turbine blades, impellers and other components.
- Surface treatment: The surface treatment of the processed parts, such as sandblasting, polishing, coating, etc., to improve the surface finish and corrosion resistance.

5. Quality control
- Process control: In the whole forging process, strict quality control is carried out, including material inspection, forging parameter control, heat treatment parameter control, processing size control, etc., to ensure that each link meets the design requirements.
- Inspection: Strict inspection of the finished turbine parts, including dimensional inspection, appearance inspection, mechanical performance inspection, non-destructive testing, etc., to ensure that the parts meet the quality standards.
Our turbine products can meet your needs for high quality, high efficiency, low energy consumption and high reliability.If you have gas turbine manufacturing needs, contact us today for our most professional services!
