Turbine Blades
Hot end components, turbine blades belong to the hot end components of aircraft engines. They need to work in a high temperature and high pressure environment and are the most difficult blades to manufacture in turbofan engines. High temperature and high pressure combustion gas expands in the turbine, driving the turbine to rotate at high speed to drive the compressor. The airflow enters the tail nozzle through the turbine outlet, where the pressure decreases and the speed increases, and finally it is discharged from the engine to generate power.
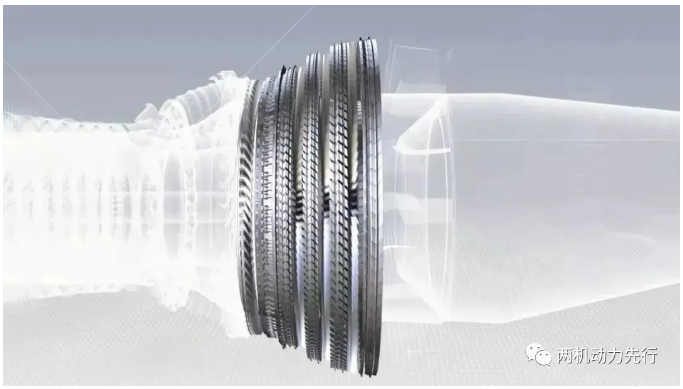
The structure and material of turbine blades are constantly upgraded. In the mid-20th century, the second-generation engines were mainly used, and the typical model was the Spey MK202, which mainly used solid turbine blades. After that, more advanced hollow turbine blades were gradually used. The fifth-generation engine F135 has adopted double-walled super-cooled/cast-cooled turbine blades.
Turbine blades are generally made of high-temperature alloys or titanium-aluminum alloys, and are processed through precision casting to form blade blanks with small excess and high quality. With the improvement of engine performance, high-pressure turbine blades have gradually developed into blades made of directional crystallization and single crystal materials.
Directional crystallization is a casting process in which the molten alloy is crystallized and solidified in the investment casting shell in the direction opposite to the heat flow. The turbine blades formed by this process have high resistance to thermal fatigue and thermal shock.
Compressor and fan blades
Cold end core components. During the operation of the engine, the blades are affected by centrifugal force, aerodynamic force generated by air and gas, thermal stress, alternating force, random load, etc., accounting for more than 30% of the workload of the entire engine manufacturing. Under the action of various loads, the blades are very prone to high-cycle fatigue and thermal fatigue. In order to ensure work quality and work efficiency, the material selection and production process of the blades have extremely high requirements.
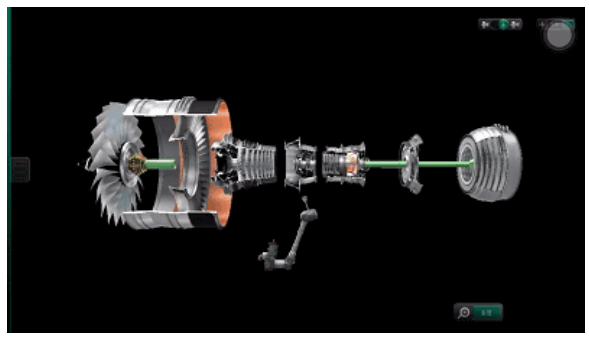

Engine blades can be divided into fan blades, compressor blades and turbine blades according to their location and function. Fan blades and compressor blades are cold end components, while turbine blades are hot end components.
The compressor blades can be divided into compressor rotor blades (working blades) and compressor stator blades (rectifier blades), and the turbine blades can be divided into turbine working blades and turbine guide blades. The fan blades initially compress the air entering the engine, and the compressed gas is divided into two paths, one entering the inner duct for further compression, and the other entering the outer duct for direct high-speed discharge to generate thrust.
The compressor blades further compress the air entering the inner duct, and the air pressure and temperature increase significantly to meet the needs of the combustion chamber. The turbine blades have the effect of expansion and decompression, which can convert the chemical energy of the gas into the mechanical energy of the turbine.
Blade materials include aluminum alloy, stainless steel, titanium alloy, high-temperature alloy and composite blades, etc. Fan and compressor blades are cold-end components with relatively low operating temperatures. They are generally made of titanium alloy, high-temperature alloy and other materials. Titanium alloy is widely used in the production of compressor blades because of its low specific gravity, high specific strength and corrosion resistance, and its outstanding contribution to weight reduction.


From the manufacturing process point of view, compressor blades are thin and easy to deform. Accurately controlling their molding accuracy and efficiently and high-quality processing are the core difficulties in the blade manufacturing process. Among all kinds of blades, compressor blades are one of the parts with the most complex surface structure and the most demanding working environment in aircraft engines.
In order to reduce the loss of air flow power, the biggest feature of compressor blades compared to other parts of the blades is their complex surface torsion and thin thickness. The complex surface torsion is specifically reflected in the different bending angles of the blade from the root to the tip. On the other hand, the thickness of the leading and trailing edges of the blade is only 0.1-0.2mm, and the contour requirements are high.
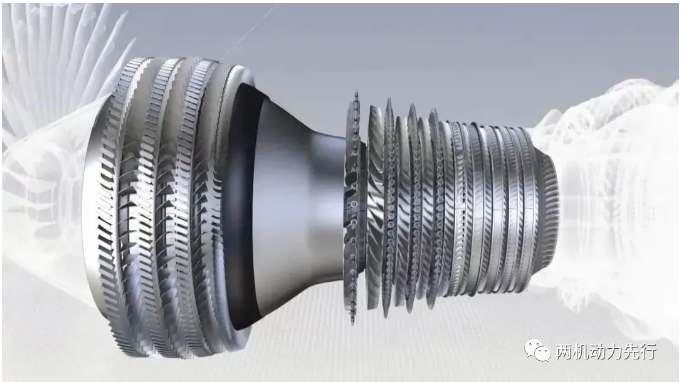

Other parts
Disk Parts
The main ones are turbine disk, compressor disk and integral blade disk. The integral blade disk structure is a new type of integrated disk structure developed on the basis of the conventional disk separation structure. It has the advantages of reducing weight, reducing levels, increasing efficiency and improving reliability. The materials are generally titanium alloy and high-temperature alloy.
The turbine disc and compressor disc are both rotor components of aircraft engines. The turbine disc is a component on aircraft engines used to install and fix turbine blades to transmit power. It is subject to complex loads in high temperature, high pressure and high speed working environment.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in our company! As a professional gas turbine parts manufacturing company, we will continue to be committed to technological innovation and service improvement, to provide more high-quality solutions for customers around the world.If you have any questions, suggestions or cooperation intentions, we are more than happy to help you. Please contact us in the following ways:
WhatsAPP:+86 135 4409 5201
E-mail:peter@turbineblade.net
