
When the turbine is working, high temperature will be generated, usually at hundreds to thousands of degrees Celsius, which requires the accessories to withstand high temperature without deformation or performance degradation.
For example, in a gas turbine, the internal pressure is high, and the turbine accessories need to have sufficient strength to withstand this pressure.
Turbine accessories will rotate at extremely high speeds and withstand huge centrifugal forces, so they need to have good mechanical properties and stability.
They may be exposed to corrosive gases or liquids produced by fuel combustion, which requires accessories to be corrosion-resistant.
Aerospace: Mainly used for high-temperature components of jet engines and turbochargers, improving engine performance and reliability.
Energy industry: Including turbomachinery components in gas turbines, nuclear power plants and fossil fuel power plants, ensuring long-term stable operation of equipment.
Chemical industry: Used to manufacture high-temperature and high-pressure equipment such as chemical reactors, pipelines and valves, and withstand the effects of highly corrosive media.
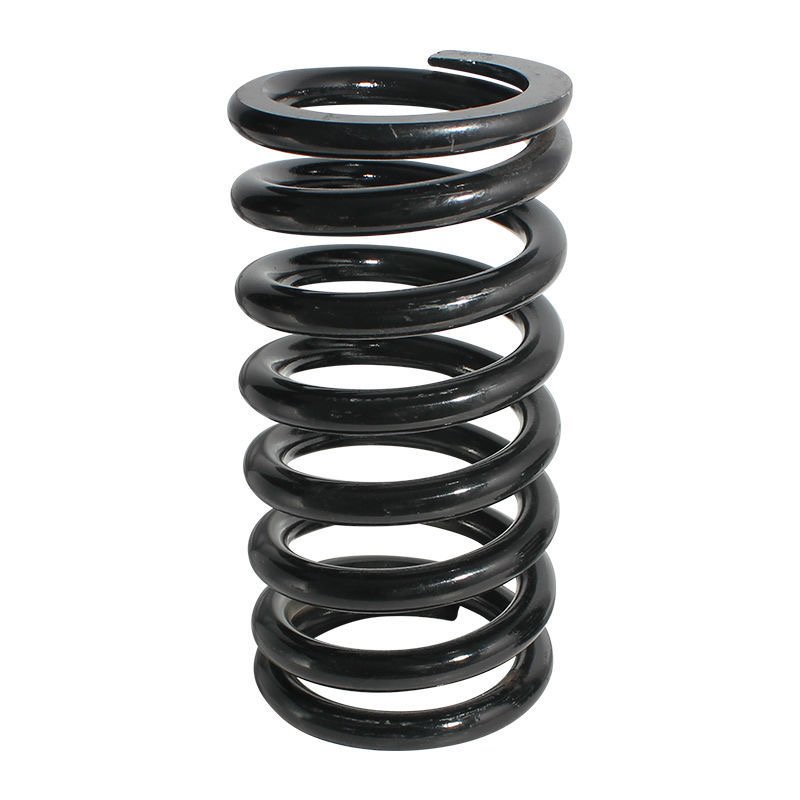
The main function of the spring in a high-temperature turbine engine is to provide mechanical compensation and vibration absorption. High-temperature alloy springs can work for a long time in a high-temperature, high-stress environment, and have good heat resistance and fatigue life. They are widely used in the connection and support of various components.
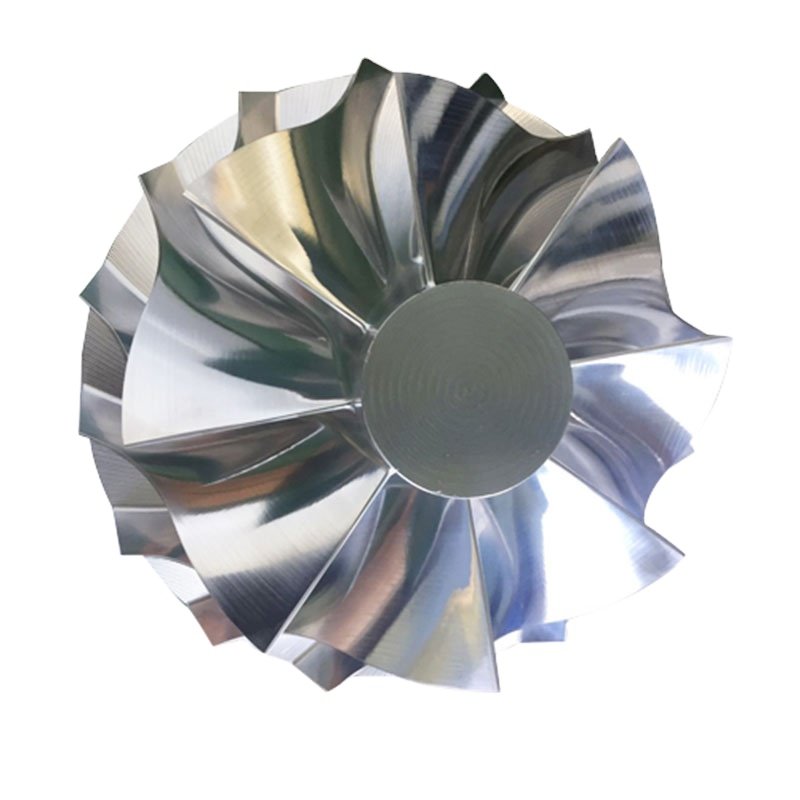




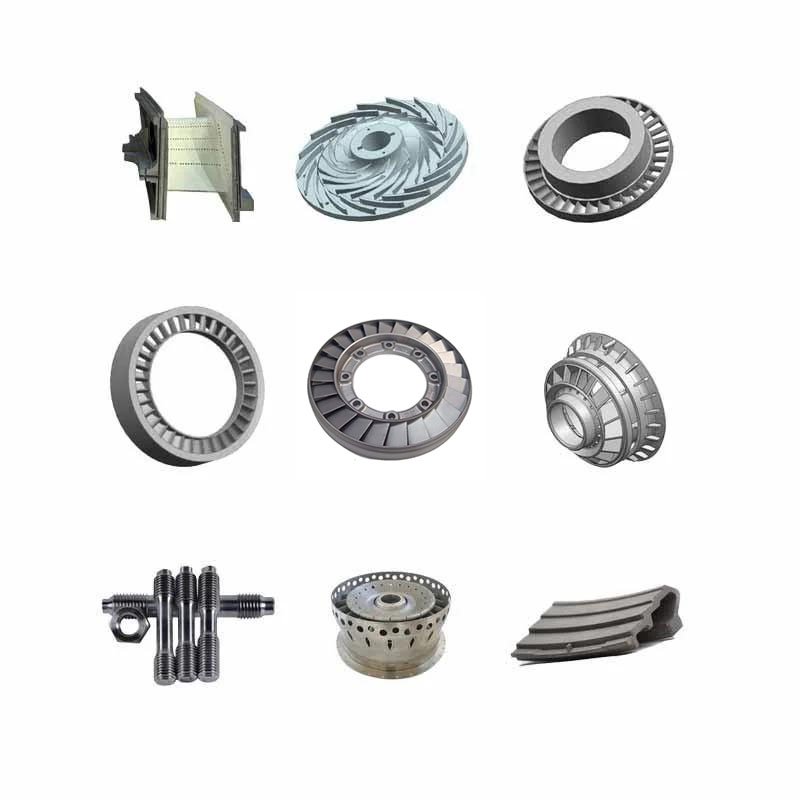
The stator is the stationary part of the turbine engine, which plays a guiding and supporting role. The stator blades are fixed to the turbine casing to change the direction of the airflow and increase the kinetic energy of the gas. The stator made of high-temperature alloys can maintain a stable state under high temperature and high pressure environments, reducing deformation and fatigue damage.
The rotor is a rotating part in a turbine engine that converts the kinetic energy of the gas into mechanical energy, thereby driving the axle and other components. The rotor blades need to operate at high speed and high temperature and high pressure, so they are usually made of high-temperature alloys to ensure their strength and durability and reduce wear and cracks during operation.
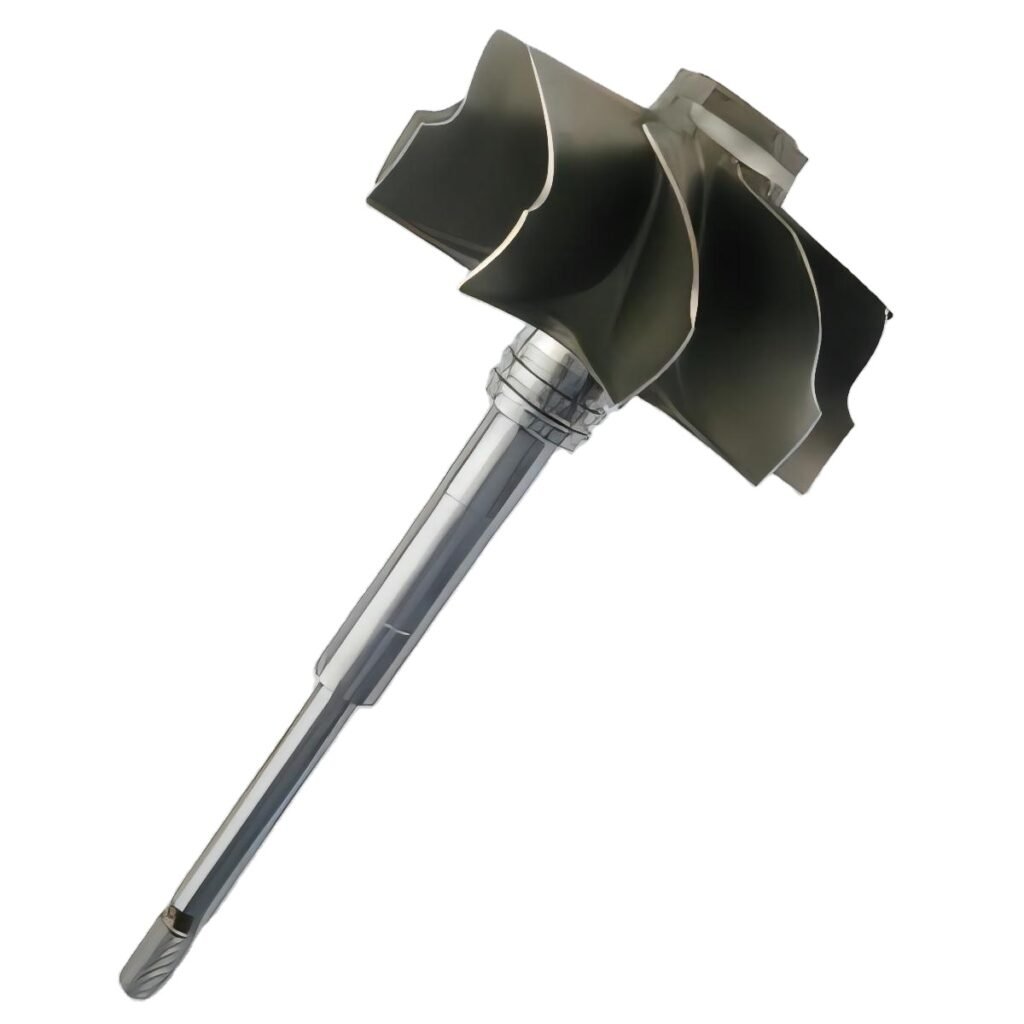




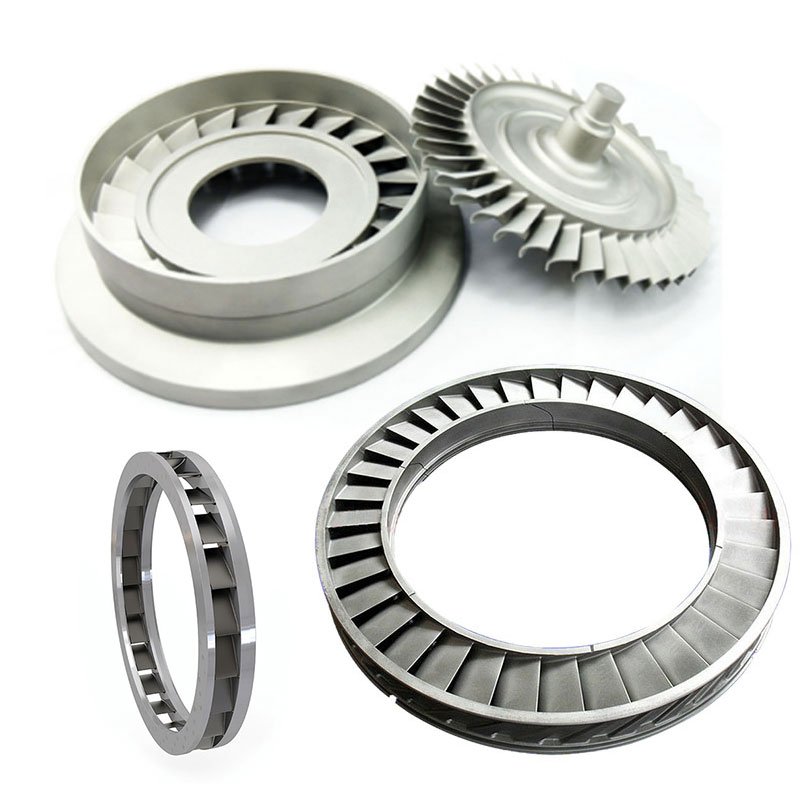
The combustion chamber is one of the core components of the engine, used for mixing and burning fuel and compressed air. High-temperature alloy combustion chambers can withstand extremely high temperatures and pressures, providing the turbine blades with the required high-energy gases while reducing combustion erosion on the metal structure.
Arc segments are part of the turbine's interior, usually near the impeller passage. They are made of high-temperature alloys to adjust and support the airflow, and work under high temperature and high pressure conditions to ensure the stability and efficiency of the turbine operation.
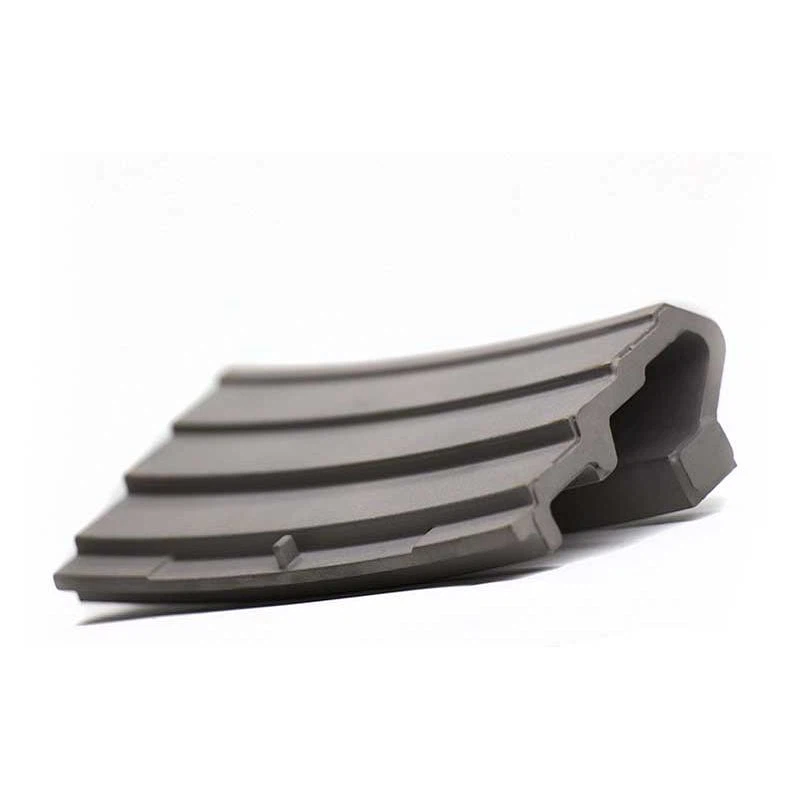


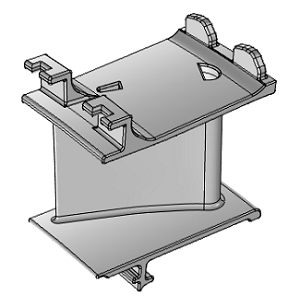

Guide vanes are fixed to the stator to guide the airflow entering the rotor. High-temperature alloy guide vanes can work efficiently in extreme environments, have high corrosion resistance and strength, and ensure accurate and stable airflow direction adjustment.
The nozzle ring is used to guide the combustion gas into the turbine to maximize energy conversion efficiency. High-temperature alloy nozzle rings have excellent heat resistance and oxidation resistance, ensuring that the structure does not deform under high temperature and high pressure conditions, extending the service life.
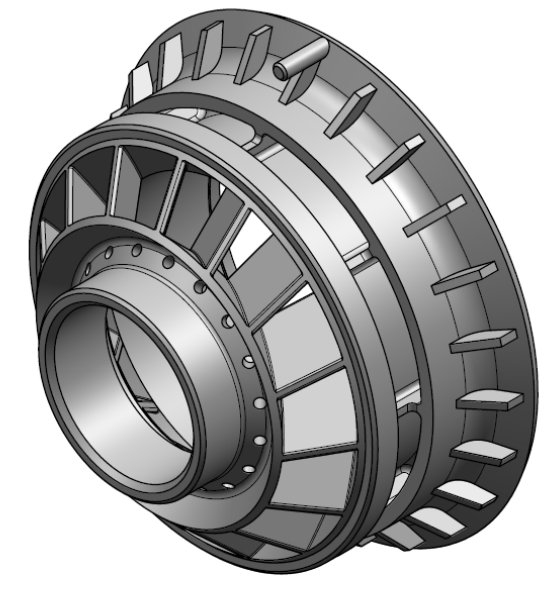




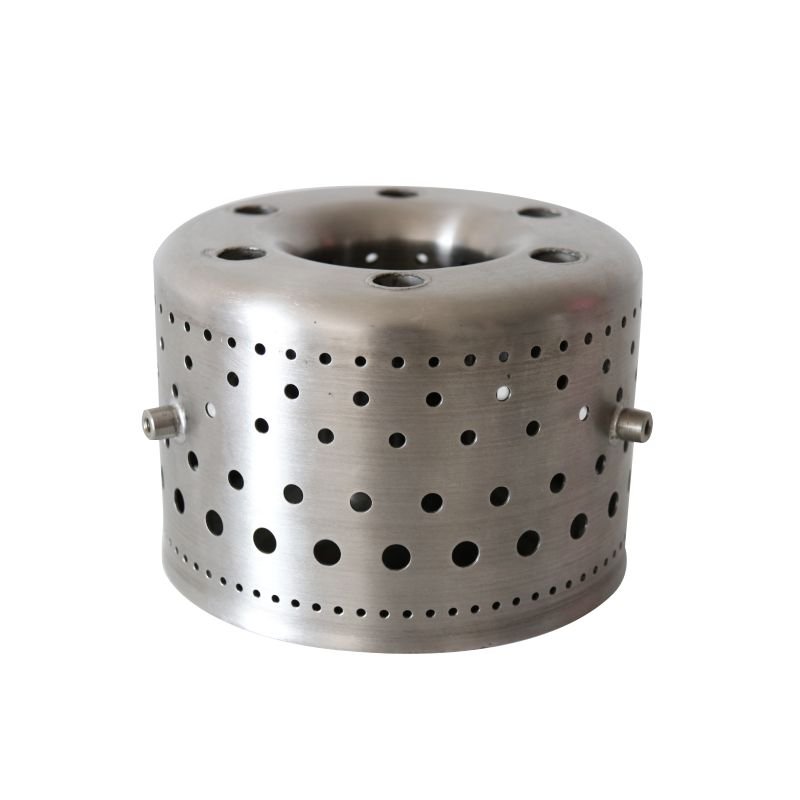
Swirler are used to enhance and maintain the turbulent state of the airflow and improve combustion efficiency. High-temperature alloy swirler have excellent thermal fatigue resistance and can work for a long time in harsh working environments to ensure complete and efficient combustion.
The diffuser is located at the rear of the turbine and is used to slow down and increase the airflow pressure. High-temperature alloy diffusers are designed to withstand the high-temperature and high-pressure airflow from the turbine, thereby ensuring efficient operation of the engine and reducing fatigue and damage.
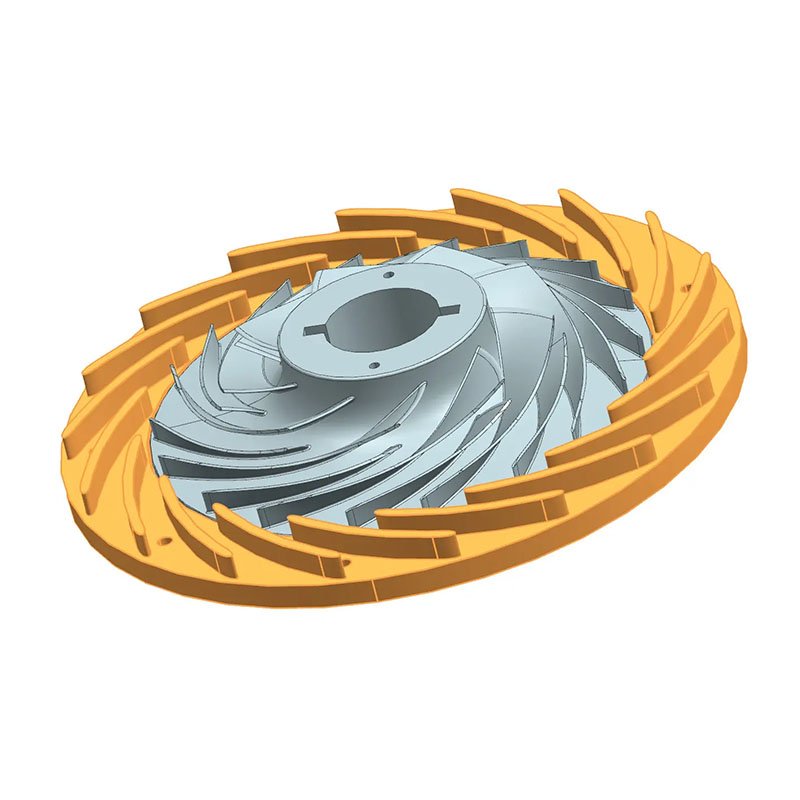


Bolts and nuts play a role in fastening and connecting in high-temperature turbine engines. High-temperature alloy bolts and nuts can maintain high strength and stability under high temperature and high pressure environments, prevent loosening and connection failure caused by thermal expansion, ensure that each component is tightly combined, and maintain the overall performance and safety of the engine.
Part numbers alone are not sufficient to ensure performance.
To guarantee precision and compatibility, please provide:
Drawings or used samples for reverse engineering.