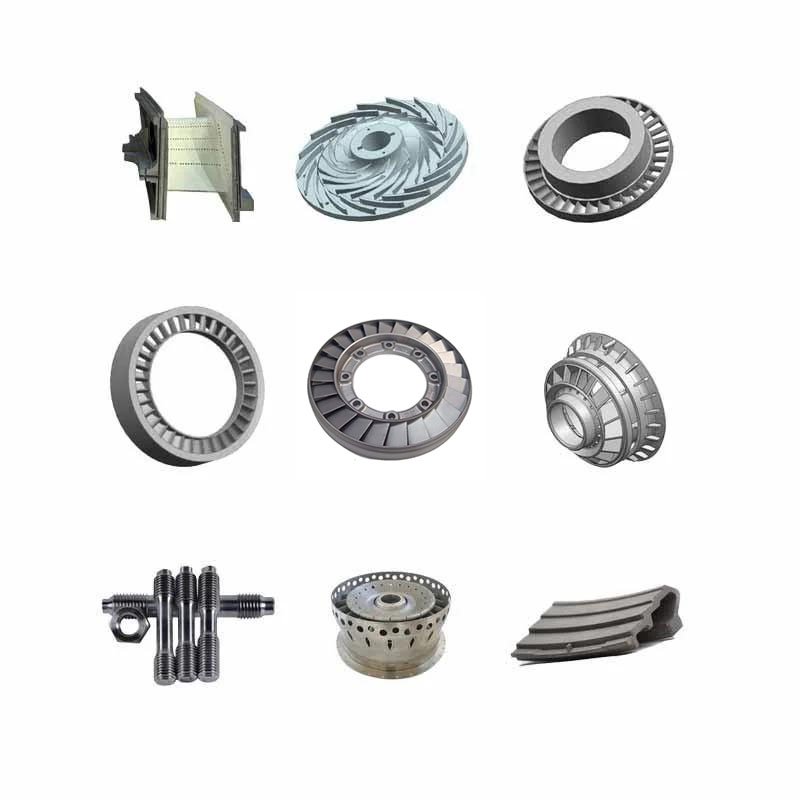

Stellite alloy is well known for its high hardness and wear resistance. This allows turbine parts to be used for a long time in high-speed rotation and high-friction environments without damage, reducing equipment maintenance and replacement frequency.
Under high temperature working conditions, Stellite alloy can maintain good mechanical properties and structural stability. This makes turbine parts suitable for applications requiring high temperature stability, such as aircraft engines and gas turbines.
The chromium and other corrosion-resistant elements contained in Stellite alloy have excellent corrosion resistance and can resist the erosion of chemical media. This makes Stellite turbine parts have long-term durability in chemical and marine environments.
Stellite alloy has excellent strength and rigidity, which can withstand the challenges of high-speed rotation and complex dynamic loads while maintaining stable performance. This is crucial for the reliability and long-term use of turbine parts.
Stellite alloy turbine parts are widely used in the following major fields:
Aerospace: used to manufacture turbine blades, nozzles and other high-temperature parts of aircraft engines.
Energy industry: especially for high temperature turbine blades and nozzles in gas turbines and turbochargers.
Chemical industry: used to manufacture corrosion-resistant blades and bearings for chemical reactors, pumps and valves.
Marine engineering: used in seawater environments for turbine impellers and other key components of ships and offshore platforms to cope with the corrosion and high pressure environment of seawater.
The process of manufacturing Stellite alloy turbine parts includes:
Investment casting: suitable for manufacturing turbine blades and other components with complex shapes and internal channels.
Machining: including roughing and finishing to ensure that blades and other components meet the designed geometric requirements and surface roughness.
Heat treatment: through processes such as solution treatment and precipitation hardening, the grain structure of the alloy is optimized and the hardness is increased to enhance mechanical properties and wear resistance.
Material properties: such as high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, high strength, etc.
Manufacturing precision: Ensure that the size and shape of the parts meet strict standards to ensure good assembly and operating performance.
Coefficient of thermal expansion: Match with other parts of the gas turbine to avoid failures caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
Wear resistance: Wear resistance is particularly important in high-speed operation and high-temperature environments.




Select materials with good wear resistance, heat resistance and corrosion resistance.
Reduce friction and stress concentration between accessories through reasonable design.
Ensure that the cooling system can effectively reduce the temperature of accessories.
Regularly check and replace severely worn accessories.
Regular inspection: Check whether the accessories have abnormal conditions such as wear, cracks, deformation, etc.
Cleaning: Remove dust, oil and impurities on the surface of the accessories and keep them clean.
Control temperature: Ensure that the operating environment temperature is suitable to avoid high temperature from damaging the accessories.
Avoid collision: Handle carefully during operation and transportation to prevent the accessories from collision.
Manage lubrication: Ensure that the accessories are properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
Perform professional inspection: Regularly have professionals use professional equipment to conduct inspections and evaluations.
Pay attention to the storage environment: When not in use, store in a dry, well-ventilated place with a suitable temperature.
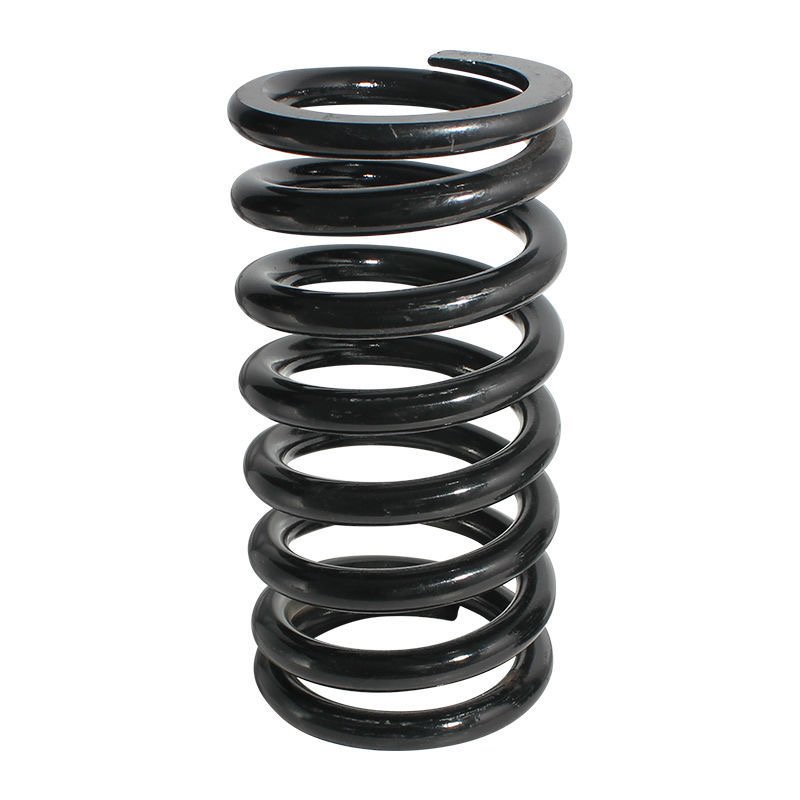
The main function of the spring in a high-temperature turbine engine is to provide mechanical compensation and vibration absorption. High-temperature alloy springs can work for a long time in a high-temperature, high-stress environment, and have good heat resistance and fatigue life. They are widely used in the connection and support of various components.




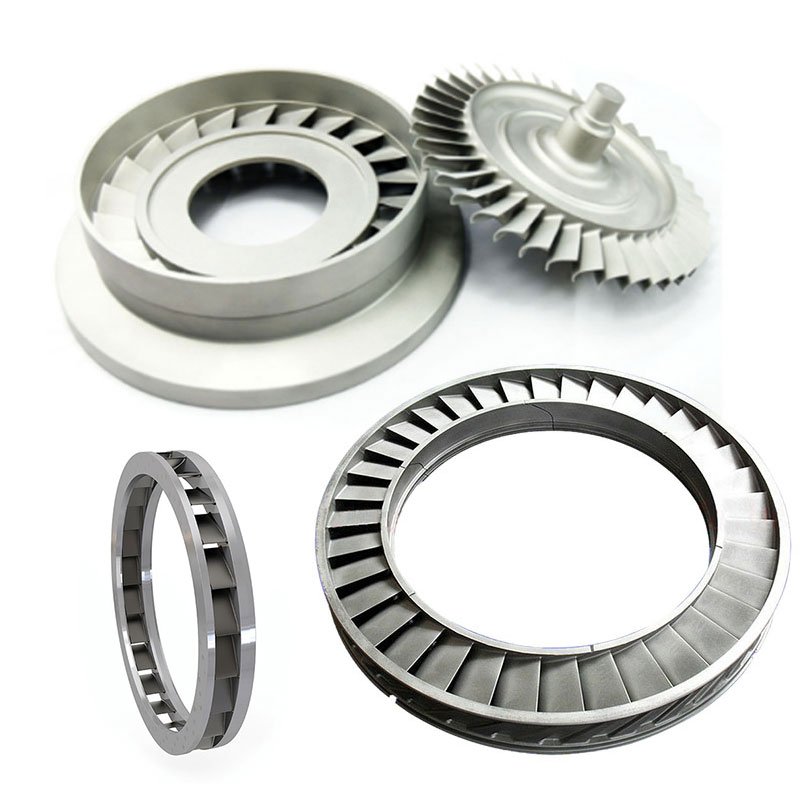
The stator is the stationary part of the turbine engine, which plays a guiding and supporting role. The stator blades are fixed to the turbine casing to change the direction of the airflow and increase the kinetic energy of the gas. The stator made of high-temperature alloys can maintain a stable state under high temperature and high pressure environments, reducing deformation and fatigue damage.
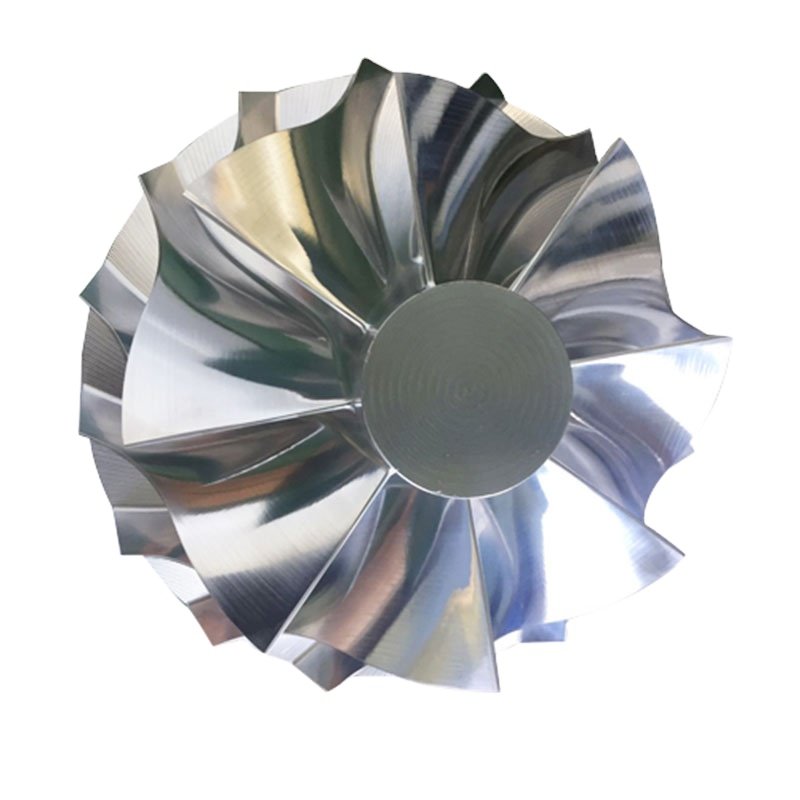
The rotor is a rotating part in a turbine engine that converts the kinetic energy of the gas into mechanical energy, thereby driving the axle and other components. The rotor blades need to operate at high speed and high temperature and high pressure, so they are usually made of high-temperature alloys to ensure their strength and durability and reduce wear and cracks during operation.
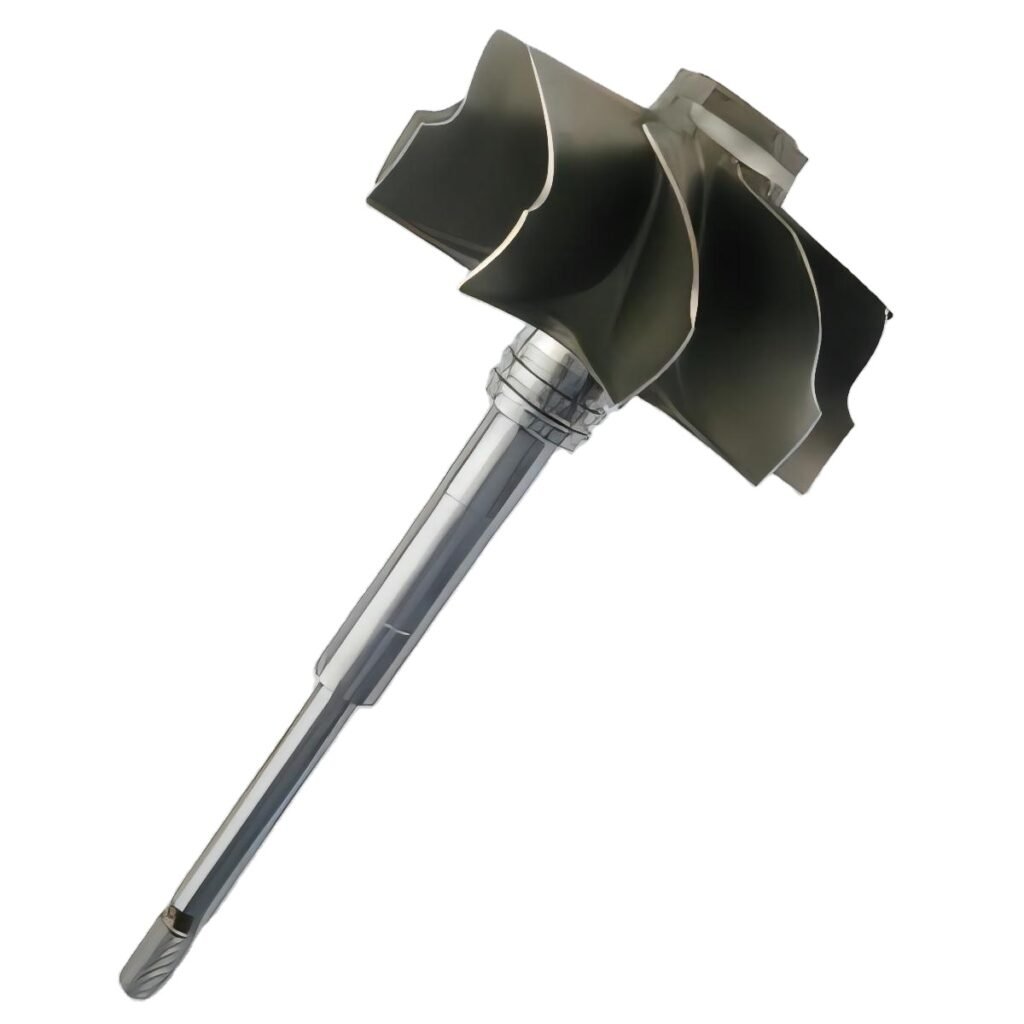
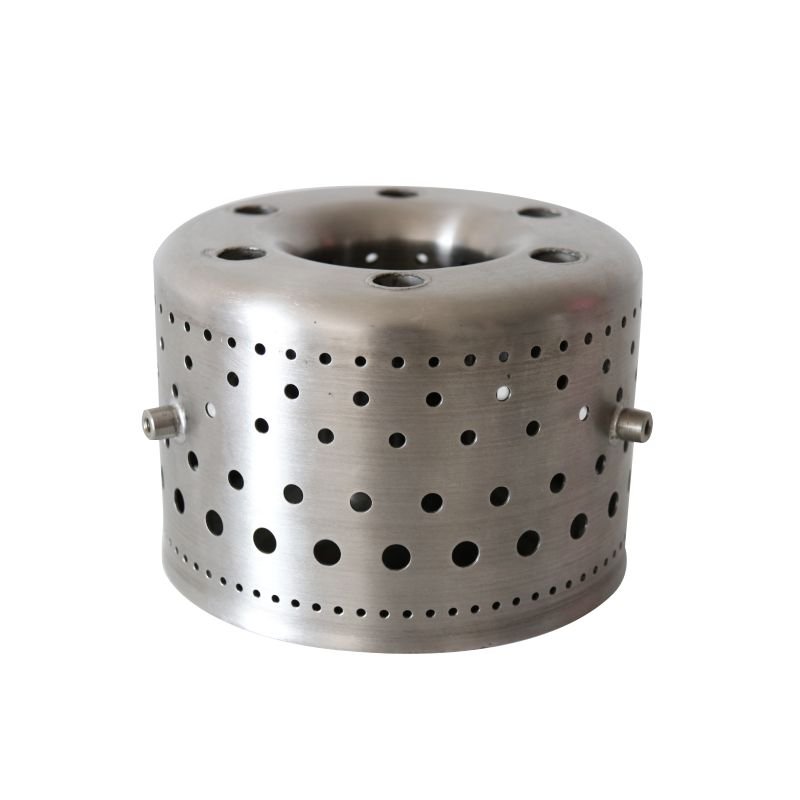




The combustion chamber is one of the core components of the engine, used for mixing and burning fuel and compressed air. High-temperature alloy combustion chambers can withstand extremely high temperatures and pressures, providing the turbine blades with the required high-energy gases while reducing combustion erosion on the metal structure.
Arc segments are part of the turbine's interior, usually near the impeller passage. They are made of high-temperature alloys to adjust and support the airflow, and work under high temperature and high pressure conditions to ensure the stability and efficiency of the turbine operation.
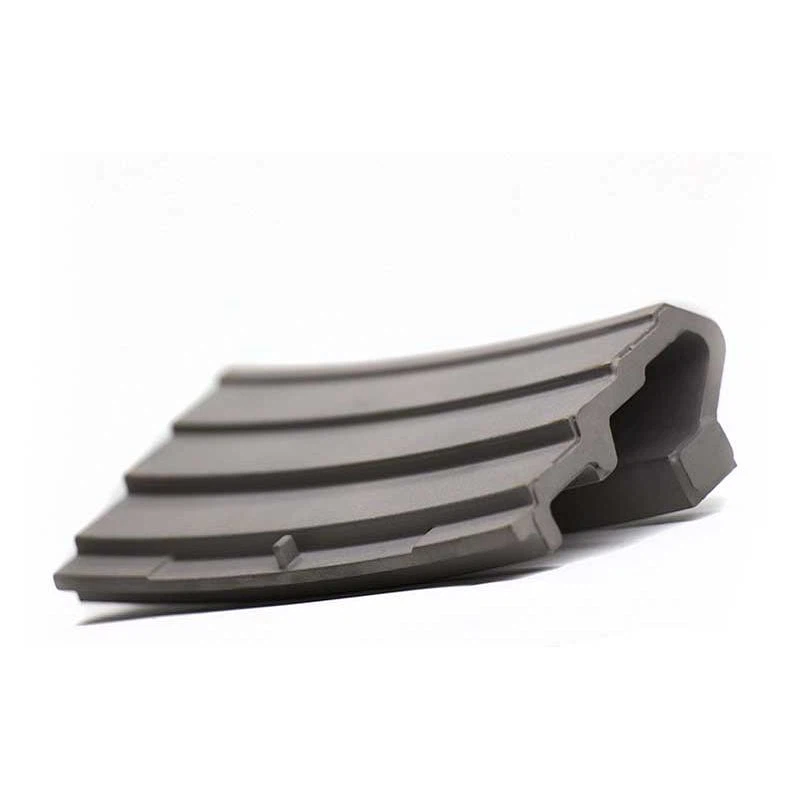



Guide vanes are fixed to the stator to guide the airflow entering the rotor. High-temperature alloy guide vanes can work efficiently in extreme environments, have high corrosion resistance and strength, and ensure accurate and stable airflow direction adjustment.
The nozzle ring is used to guide the combustion gas into the turbine to maximize energy conversion efficiency. High-temperature alloy nozzle rings have excellent heat resistance and oxidation resistance, ensuring that the structure does not deform under high temperature and high pressure conditions, extending the service life.
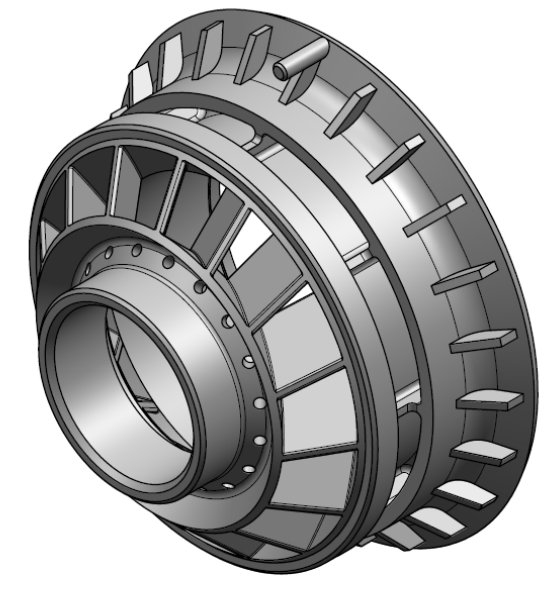






Swirler are used to enhance and maintain the turbulent state of the airflow and improve combustion efficiency. High-temperature alloy swirler have excellent thermal fatigue resistance and can work for a long time in harsh working environments to ensure complete and efficient combustion.
The diffuser is located at the rear of the turbine and is used to slow down and increase the airflow pressure. High-temperature alloy diffusers are designed to withstand the high-temperature and high-pressure airflow from the turbine, thereby ensuring efficient operation of the engine and reducing fatigue and damage.




Bolts and nuts play a role in fastening and connecting in high-temperature turbine engines. High-temperature alloy bolts and nuts can maintain high strength and stability under high temperature and high pressure environments, prevent loosening and connection failure caused by thermal expansion, ensure that each component is tightly combined, and maintain the overall performance and safety of the engine.
Part numbers alone are not sufficient to ensure performance.
To guarantee precision and compatibility, please provide:
Drawings or used samples for reverse engineering.