





Material Features: Inconel alloy has excellent high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance and creep resistance.
Equiaxed crystal casting suitability: Inconel alloy is suitable for equiaxed crystal casting process, which can manufacture turbine parts with excellent performance in high-temperature environment. Equiaxed crystal casting can improve the density and mechanical properties of the material.
Material features: Hastelloy alloy has excellent corrosion resistance and high temperature strength, suitable for extreme environments.
Applicability of equiaxed crystal casting: Hastelloy alloy is suitable for equiaxed crystal casting process, which can manufacture turbine accessories with excellent performance in corrosive and high temperature environments. Process control requirements are high to ensure material performance.
Material Features: Titanium alloy has excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance.
Equiaxed crystal casting suitability: Titanium alloy is suitable for equiaxed crystal casting process, which can manufacture high-strength and lightweight turbine parts. However, the high reactivity of titanium alloy requires casting under inert atmosphere or vacuum conditions to prevent oxidation and contamination.
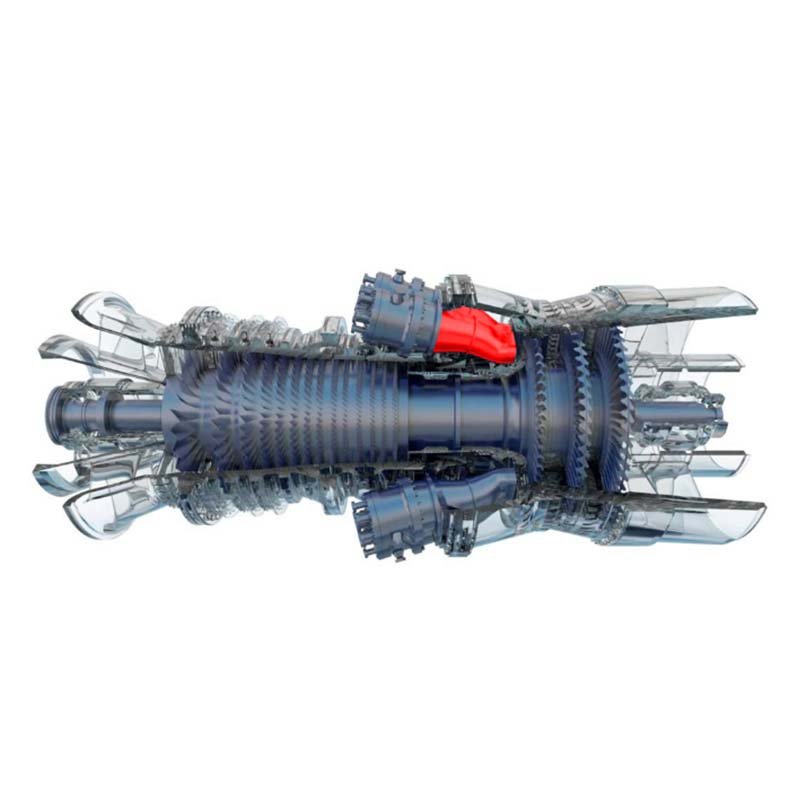
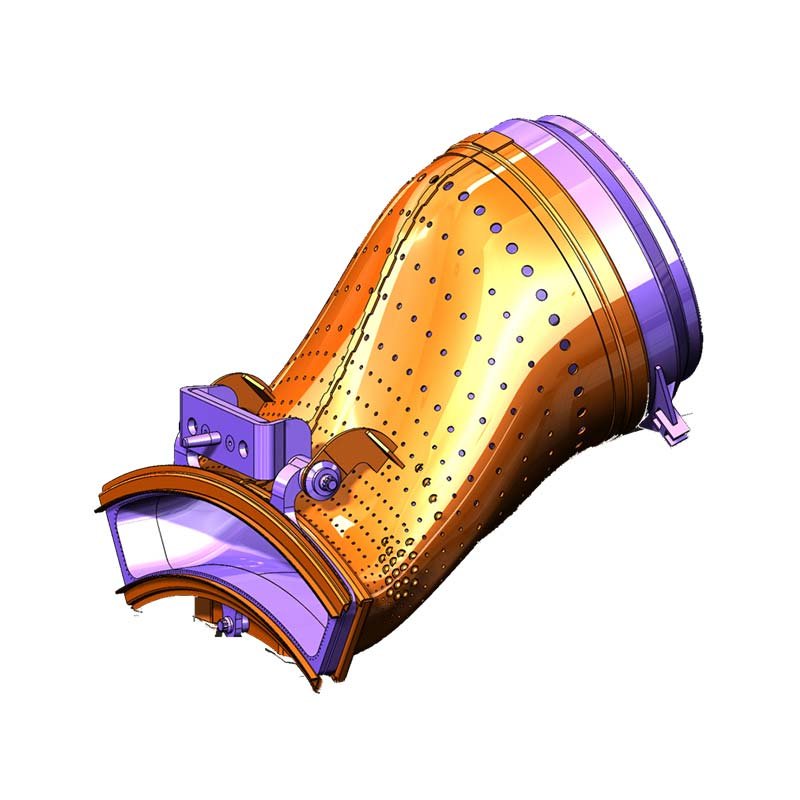
The transition section needs to withstand extremely high operating temperatures, usually between 1200°C and 1500°C or even higher. Therefore, material selection is critical.
In order to maintain its structural integrity, the transition section often requires a complex internal cooling system, such as air cooling channels.
Long-term exposure to extreme conditions requires the transition section to have excellent durability and reliability to reduce maintenance costs and downtime.
The duct’s design minimizes pressure losses and turbulence, ensuring a smooth transition of gases with minimal energy dissipation.This optimized flow is crucial for maximizing engine efficiency and performance.Poorly designed ducts can lead to significant energy losses and potential damage to downstream components.
Transition ducts often connect components with different cross-sectional areas or geometries.The duct’s design gradually changes the shape of the airflow path, facilitating a smooth transition between these disparate components.
In some cases, the transition duct plays a role in managing the temperature of the gases.The design and materials may be chosen to help control heat transfer and prevent excessive heating of adjacent components.
The transition duct must withstand the high temperatures, pressures, and potentially corrosive environments found within the gas turbine engine.Robust materials and construction techniques are essential for ensuring structural integrity and preventing failure.
Part numbers alone are not sufficient to ensure performance.
To guarantee precision and compatibility, please provide:
Drawings or used samples for reverse engineering.