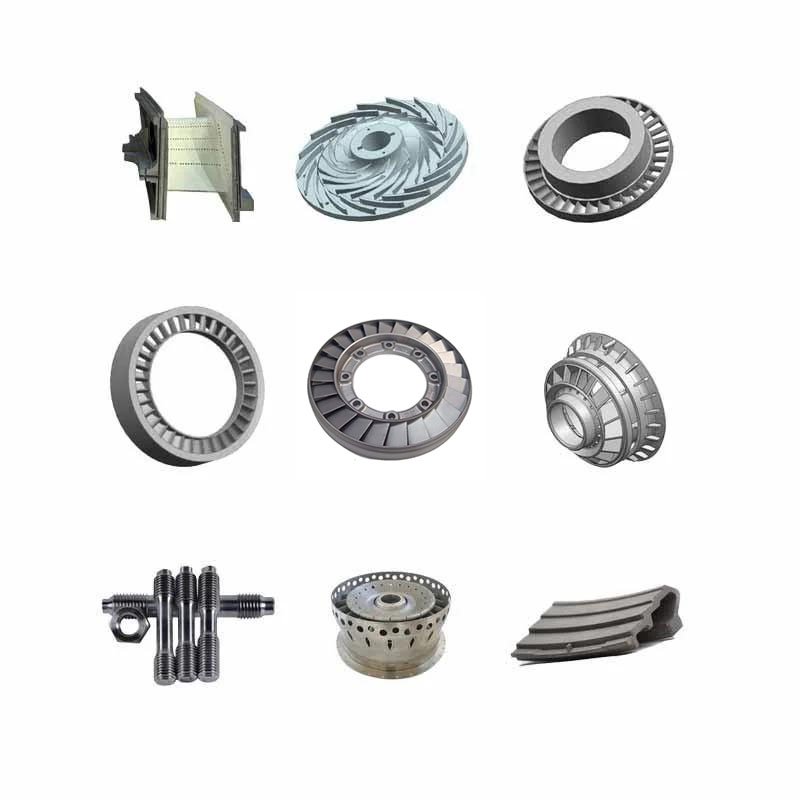

Turbine blades are key components in gas turbines, used to receive kinetic energy from high-temperature and high-pressure airflow, drive the turbine disc to rotate, and thus drive the mechanical device to work.
The turbine disc is one of the main rotating components in the turbine, responsible for supporting the turbine blades and transmitting kinetic energy, converting gas power into mechanical power.
The stator is a stationary component in the gas turbine, used to fix the guide airflow, so that it interacts with the turbine blades and improves the energy conversion efficiency.
The rotor is a rotating component in the gas turbine, including the turbine disc and the compressor rotor, responsible for receiving and transmitting kinetic energy to drive the mechanical device to work.
The turbine nozzle is one of the key components in the gas turbine, used to guide high-speed airflow, control the flow rate and direction of the airflow, and improve the kinetic energy conversion efficiency.
The guide vane, also known as the guide wing, is located in the turbine and is used to control the flow direction and speed of the airflow, optimize the entry angle of the airflow, and improve the efficiency of the turbine.
A segment is a component in a turbine, commonly found in the compressor part of a gas turbine, used to increase the kinetic energy of the gas flow and reduce pressure.
Springs play various roles in gas turbines, such as maintaining the position of components and providing elastic support.
Bolts and Nuts are used to connect and fix the various components of a gas turbine to ensure tight connection and stability between components.
Directional solidification aligns the grains in the direction of force, improving the strength and rigidity of the material.
Able to maintain stable performance in high temperature environments, suitable for high temperature applications such as turbine engines.
Turbine parts with complex shapes can be produced to meet high precision requirements.
Directional solidification reduces grain boundaries and defects, improving the fatigue life of turbine parts.
Regarding the use temperature, different types of turbine parts and application scenarios will be different. Generally speaking, some advanced turbine parts can work at temperatures of hundreds or even thousands of degrees Celsius. For example, turbine parts used in aircraft engines may have to withstand extremely high temperatures, while in other fields the temperature requirements may be relatively low. The specific use temperature will also be affected by many factors such as material properties and cooling system.
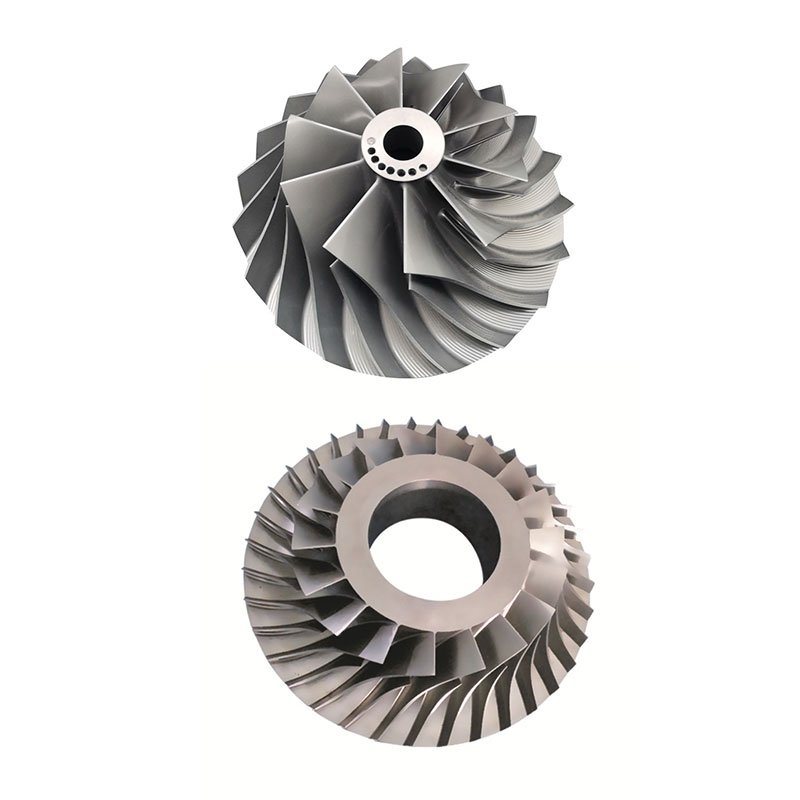









Part numbers alone are not sufficient to ensure performance.
To guarantee precision and compatibility, please provide:
Drawings or used samples for reverse engineering.